HIGHLIGHTS-
• Pixxel has successfully launched its first full-fledged commercial satellite, called ‘Shakuntala’.
• It carries one of the highest resolution hyperspectral commercial cameras ever flown to space.
• Shakuntala will begin collecting data just a few weeks after its launch, revealing the planet’s hidden changes.
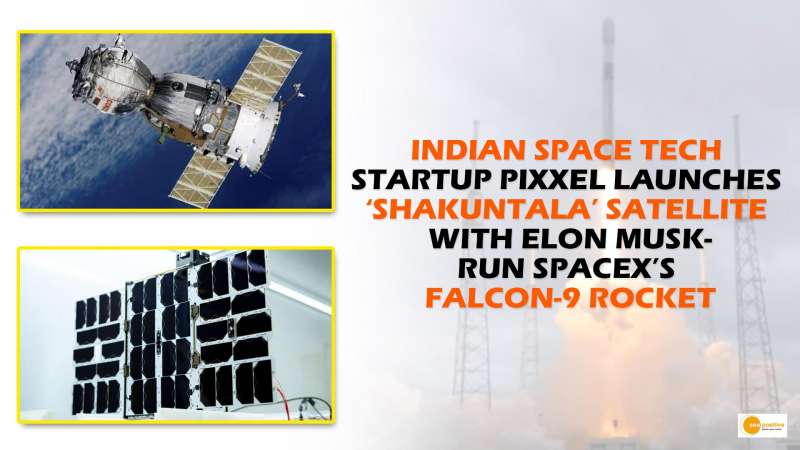
The Spacetech startup, Pixxel has successfully launched its first full-fledged commercial satellite, called ‘Shakuntala’. The Shakuntala is launched using SpaceX’s Falcon-9 rocket, which is run by Elon Musk.
The satellite carries one of the highest resolution hyperspectral commercial cameras ever flown to space, bringing the company one step closer to developing a 24×7 health monitor for the planet.
Special Features of the Shakuntala
Shakuntala (TD-2) is a small satellite weighing less than 15 Kg. Shakuntala is capable of capturing orbital images in more than 150 bands of color from the visible and infrared spectrum with a resolution of 10-meters per pixel, which outperforms the specificity of 30-meter per pixel hyperspectral satellites launched by a few select organizations such as ESA, NASA, and ISRO.
Shakuntala to reveal invisible secrets of planet
Shakuntala will begin collecting data just a few weeks after its launch, revealing the planet’s hidden changes such as deforestation, natural gas leakages, pollution, poor crop health, and melting ice caps.
Pixxel’s journey of success
Life has gone full circle for Pixxel according to its CEO Awais Ahmed. Pixel went from being one of the few finalists in the SpaceX Hyperloop Pod Competition to launch a satellite as part of SpaceX’s fourth rideshare mission in 2017.
24×7 health monitor for the planet
‘Shakuntala,’ carries one of the highest resolution hyperspectral commercial cameras ever flown to space, bringing the company one step closer to developing a 24×7 health monitor for the planet, according to the company.
One step closer to its ambitious aims
This launch, which took place on SpaceX’s Transporter-4 mission from Cape Canaveral, Florida, gets the company closer to completing its ambitious aim of assembling one of the world’s most advanced constellations of low-earth-orbit imaging satellites.